Problem’s Website
- 紧急集合 / 聚会
Solution
- 这是一道求树上三点的最短距离题,我们知道,树上两点的最短距离为两点到两点的LCA的距离之和,那么三个点的最短距离如何求呢?
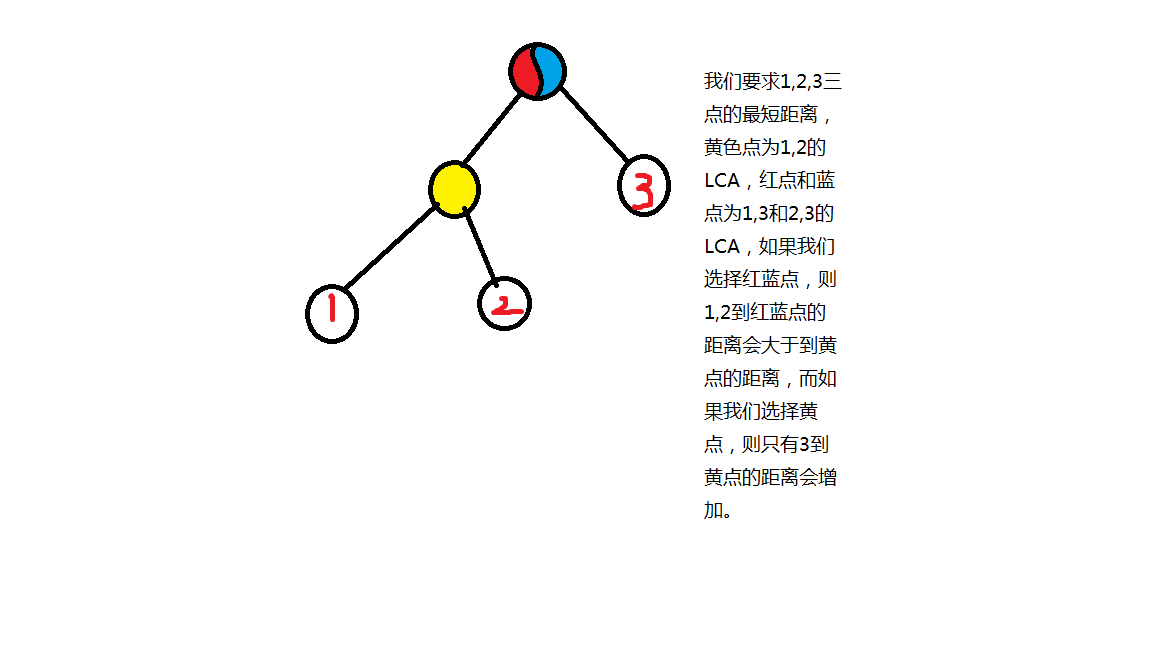
- 肯定也和LCA有关,假设我们现在有a,b,c三个点,aa = LCA(a, b),bb = LCA(b, c),cc = LCA(c, a),结论是:aa,bb,cc中不同与其他两点的点为最短路径的必经之点,至于证明,本蒟蒻不太会,胡乱证明一下,见下图:
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
using namespace std;
int sc() {
int xx=0,ff=1; char cch;
while(cch<'0'|| cch>'9') {
if(cch=='-') ff=-ff; cch=gc;
}
while(cch>='0'&& cch<='9') {
xx=xx*10+(cch-48); cch=gc;
}
return xx*ff;
}
struct TREE {
int next,to;
}edge[Maxn*2];
int cnt,n,m;
int head[Maxn*2],deep[Maxn];
int f[Maxn][21];
namespace DY {
void ADD(int from,int to) {
edge[++cnt].next=head[from];
edge[cnt].to=to;
head[from]=cnt;
}
void D_F(int son,int fa) {
deep[son]=deep[fa]+1;
for(int i=1; i<=19; i++)
f[son][i]=f[f[son][i-1]][i-1];
for(int i=head[son]; i; i=edge[i].next) {
int to=edge[i].to;
if(to==fa) continue;
f[to][0]=son;
D_F(to,son);
}
}
int LCA(int x,int y) {
if(deep[x]<deep[y]) swap(x,y);
for(int i=20; i>=0; i--) {
if(deep[f[x][i]]>=deep[y])
x=f[x][i];
if(x==y) return x;
}
for(int i=20; i>=0; i--) {
if(f[x][i]!=f[y][i])
x=f[x][i],y=f[y][i];
}
return f[x][0];
}
void main() {
n=sc(); m=sc();
for(int i=1; i<n; i++) {
int u=sc(),v=sc();
ADD(u,v); ADD(v,u);
}
D_F(1,0);
while(m--) {
int aa=sc(),bb=sc(),cc=sc(),d1;
int a1=LCA(aa,bb);
int b1=LCA(aa,cc);
int c1=LCA(bb,cc);
if(a1==b1) d1=c1;
else if(a1==c1) d1=b1;
else if(b1==c1) d1=a1;
int res=deep[aa]+deep[bb]+deep[cc]-deep[a1]-deep[b1]-deep[c1];
printf("%d %d\n",d1,res);
}
}
};
int main() {
DY::main();
return 0;
}
rp++