$Problem’s$ $Website$
$Solution$
这道题是一道既考思想有考代码能力的好题,能学到不少东西。
这道题我是用$fhq-Treap$ $+$ 线段树 做的,思想类似于模板 最长公共子序列,这道题我写了一篇题解,大家可以先去查看一下,当然也可以不看。。。
大体说一下做法
1.关于维护序列
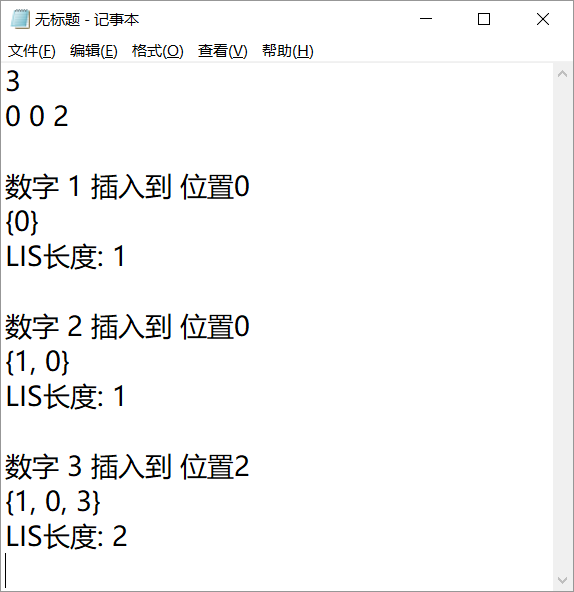
首先要把样例搞懂,所以我先把样例解释一下,见下图:
我们发现,将一个数组$x$插入到位置$i$,如果位置$i$已经有数字了,那么要进行右移,那么平衡树自然是维护序列的不二选择了,因为我暂时不会$Splay$,所以我用的是$fhq-Treap$。
对于$fhq-Treap$来说,有一点要注意,就是分裂的对象,这道题我们要以子树的大小为对象进行分裂。
2.求$LIS$
因为数据肯定不重复,所以我们可以用类似于离散化的方式来求$LIS$。
也就是用一个数组$a[x]$来记录数字$x$出现的位置,我们从小到大枚举 (因为要求$LIS$),每次求出从$1$到当前数字位置的前一个的$LIS$长度,$+1$后更新答案 (因为当前数一定比前面的数大),最后把当前位置的$LIS$记录下来。
上面的操作就是单点修改和区间最值,那么,线段树搞定!
$Code$
1 | //Coded by dy. |
$rp++$